Aware Developer Documentation
Aware's cloud-based platform works to ingest, normalize, secure and enrich human-generated text for analysis. Leverage Aware's functionality in organizational workflows via API to enhance how your teams utilize Aware today.
Platform Overview
Aware's data platform consists of multiple layers that work together to produce insights that can be leveraged by end users and external systems via Aware's Context API.
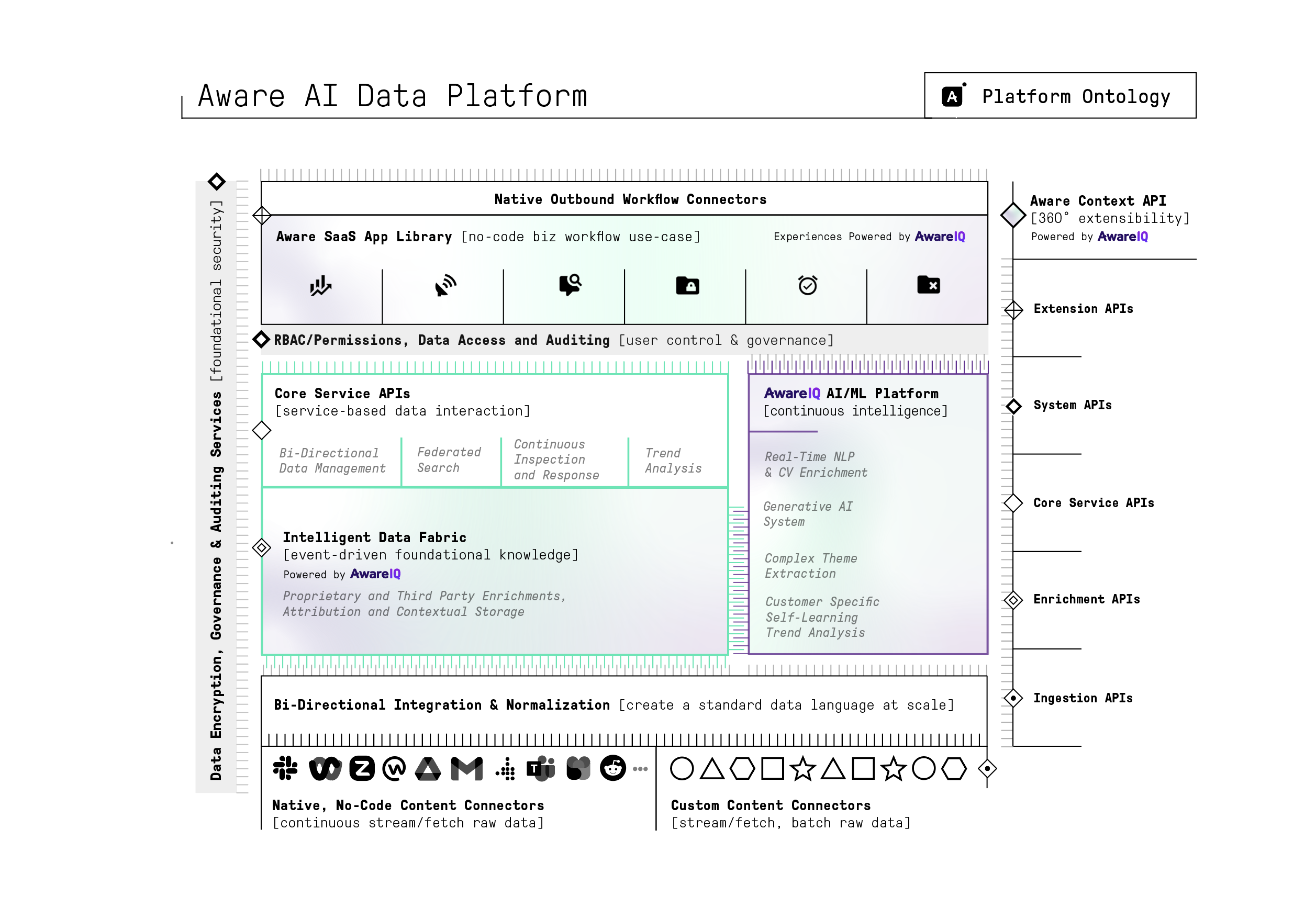
Ingestion and Normalization
The ingestion layer consists of both native and custom data integrations that allow customers to ingest their application data for enrichment and use within Aware's applications. Native integrations use near-real-time ingestion to optimize for use cases that require urgent analysis of data.
Once the data has been ingested, message, file and other types of content are normalized into a proprietary schema that allows for standardized processing further downstream. Through this normalization, Aware users are able to derive insights across different types of content from multiple sources without having to transform the content themselves.
Contextualization
During normalization, Aware organizes user generated content into content objects. Content objects are then indexed and in a variety of ways to assist with our historical search functionality and other data management activities. These relationships also form the foundation for filtering data when performing analysis against this data.
Enrichment and Attribution
The data enrichment and attribution layer labels all incoming messages, files and other human-generated text using a variety of purpose-built, proprietary ML models and other classifications, including but not limited to:
- Sentiment
- Toxicity
- Language
- Extracted Themes
- Directory Attributes
- Custom user-defined keywords and regular expression patterns
These labels are used for data filtering, triggering alerts and for granular analysis in Aware's applications.
Data Fabric Sub-systems
Once all foundational processing and enrichment has occurred, content stored in Aware is then optimized in a variety of systems to make data management at scale possible for applied use.
- Data Retention is able to perform remediation operations on both Aware's data storage as well as natively integrated platforms (when the native platform allows for such operations). This is the foundation for data removal operations and allows Aware's customers to manage their data in a variety of ways.
- Federated Historical Search powers a variety of applications that require robust, granular search capabilities at scale.
- Proactive Evaluation is where near real-time analysis occurs post normalization and contextualization. This sub-system primarily supports Aware's Signal application for a variety of use cases related to urgent analysis of content that results in in-workflow alerting and notification.
- Trend Analysis evaluates changes in content volume and attributes, providing aggregated metrics that can be used for a variety of use cases across Aware's applications.
SaaS Application Layer
Aware's application layer provides a variety of functionality for customizing the way end users interact with their organization's content and data. Custom data classification as defined within the Signal app is used to label content for use in Signal notification and alerting workflows. Signal policy rules can be used to identify content containing specific keywords, regular expression patterns, sensitive data elements including secrets, and a variety of models can be used to classify image files as NSFW, screenshots, or to extract text from image files using optical character recognition (OCR). These conditions can be combined using boolean logic to build complex rules that are then used to trigger a Signal event which can be used in a variety of workflows including:
- Notifying the content author with custom information like coaching materials
- Notifying a specified end user regarding the triggered event
- Removing the content from the native platform
- For Slack messages, content can be tombstoned (quarantined) within the Slack workspace, reviewed on Aware's platform and either released or permanently deleted
Other Aware applications include:
- Search and Discover which allows for efficient and robust search against ingested content by author/user, keyword, platform group and/or time. Searches can also be specified by author and recipient. As well, Search and Discover utilizes Aware's proprietary AI models to further filter search results based on sentiment, toxicity, and a variety of other filters. Once your search has completed you can bulk export results in many formats, including .csv, .dat, .pdf or RSMF (Relativity Short Message Format - commonly used in the eDiscovery space).
- Spotlight and Custom Reporting extracts themes, sentiment and toxicity trends, and organizational network insights to provide further understanding of a customer's data.
- A Data Management suite that includes:
- Retention which can be used to manage this data in a granular way from an archival perspective
- Data Hold which is used to retain data for matters requiring recordkeeping for legal or investigative purposes
- User Data Removal which can be utilized for regulatory actions requiring organizations to maintain an individual's data in a certain manner.
Permissions and Access Control
Because of its sensitivity, tight controls are placed on what content an Aware user can monitor or search. Custom roles are available for managing users along with granular permissions and data access controls. Together these elements work to provide effective access to what an end user needs without compromising privacy and security controls.